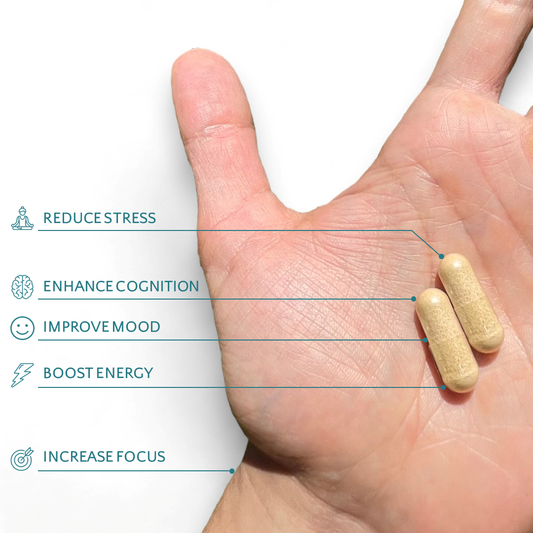
The mention of "chocolate" instantly evokes a cascade of delightful sensations, symbolizing one of the purest forms of joy in life. Its universal charm transcends ordinary indulgence, unfolding into a deep historical and cultural narrative, intertwined with the journey of the cacao plant—a journey as enchanting and rich as the flavour it yields.
This complex story unfurls in the lush Amazonian rainforests of Central and Upper America, cradle to the Olmec and Mokaya civilizations. These ancient cultures were among the first to cultivate the cacao tree, treasuring its beans over 4,000 to 5,000 years ago. This knowledge was inherited by the Mayans, who exalted the cacao plant for its divine origins.
They named it “Ka'kau” (heart blood) and “Chokola'j” (to drink together), celebrating it as a gift from the gods, a sacred embodiment used to create humanity.
With its journey across the Atlantic, cacao did more than just revolutionize European palates; it carried with it the profound, spiritual essence of Mesoamerican cultures. Presently, cacao is lauded not only as the precursor to chocolate but also as a nootropic superfood.
From its ancient Mayan origins to its current status among health aficionados, cacao's odyssey is a testament to its timeless allure as the "food of the gods." Contemporary science now corroborates the ancient esteem for cacao.
Laden with flavonoids, essential nutrients, and compounds that elevate mood, cacao is a more than a cherished chocolate, emerging as a potent enhancer of cognitive function, emotional health, and overall well-being.
Contents
- What is Cacao?
- Cacao as a Nootropic
- Chemical Composition of Cacao
- Scientific Evidence on Cacao's Benefits
- Health Benefits Beyond Cognition
- How to Use Cacao
- Safety and Side Effects
A Beginner's Guide to Cacao as a Natural Nootropic

What is Cacao?
Cacao, derived from the seeds of the Theobroma cacao tree, is renowned not just as the primary ingredient of chocolate but also for its health benefits, especially in its least processed forms.
The name itself, originating from Greek, translates to "food of the gods," underscoring the revered status cacao has held through history.
Native to the tropical regions of Central and South America, cacao's legacy as a valuable and cherished commodity dates back to ancient civilizations like the Olmecs, Mayans, and Aztecs.
These cultures not only consumed cacao in various forms but also attributed to it significant cultural, spiritual, and medicinal value.
Historical Context and Traditional Uses
The story of cacao is as rich and deep as its flavor, with evidence of its use dating back to 1750 BC in Mesoamerica.
The Aztecs, who inherited the cacao culture from their predecessors, considered it a divine gift and used it extensively in religious rituals, as a currency, and as a health elixir.
Aztec Emperor Montezuma famously consumed large quantities of a cacao-based beverage to increase stamina and vitality, highlighting early recognition of its beneficial properties.
European encounter with cacao led to its global spread, transforming it into the chocolate we know today. However, this journey also saw cacao's essence being diluted and modified to suit different palates and purposes.
Despite this, the original, less processed forms of cacao have retained their status as a powerful source of nutrition and wellness, influencing modern dietary habits and scientific research.
Chemical Composition of Cacao
The allure of cacao extends far beyond its rich flavor, rooted deeply in its complex chemical composition that makes it not just a culinary delight but a potent natural supplement.
With over 300 compounds contributing to its taste, aroma, and health benefits, cacao stands out in the realm of superfoods, particularly for its dense concentration of bioactive compounds.
- Flavanols: At the core of cacao's health-promoting properties are its flavanols, primarily epicatechin and proanthocyanidins. These polyphenolic compounds act as powerful antioxidants, offering protection against oxidative stress by neutralizing harmful free radicals. The antioxidative capacity of cacao flavanols not only contributes to reducing the risk of chronic diseases but also enhances cerebral blood flow, blood vessel elasticity, and decreases blood pressure, underscoring cacao's role as a strong anti-inflammatory agent.
- Neurotransmitter Stimulation: Cacao uniquely influences the brain's neurochemistry. It stimulates the release of several critical neurotransmitters, enhancing mood, boosting learning, memory, and overall cognitive function. Phenylethylamine (PEA) in cacao boosts focus and awareness, while anandamide, known as the bliss molecule, promotes feelings of well-being. Tryptophan, a precursor to serotonin, alongside theobromine, enhances mood and can explain chocolate's aphrodisiac qualities.
- Nutrient-Rich Profile: Beyond flavanols, cacao is a treasure trove of essential nutrients. It is rich in magnesium, iron, potassium, and calcium, supporting overall health from muscle function to bone strength. Additionally, the presence of caffeine and theobromine offers mild stimulant effects, enhancing alertness without the intensity or crash associated with coffee.
- A Prebiotic Powerhouse: Cacao's benefits even extend to gut health, acting as a prebiotic that fosters a healthy microbiome. This not only aids in digestion and absorption of nutrients but also plays a role in mood regulation through the gut-brain axis, further amplifying cacao's mood-enhancing properties.
- Beyond Antioxidants: Cacao's chemical makeup is a testament to its status as a superfood. The presence of unique compounds like theobromine, which contributes to cacao's mild stimulant effect, and phenylethylamine, which can boost mood and focus, showcases the multifaceted benefits of this ancient food. Furthermore, cacao's rich antioxidant profile, highlighted by its high 'total antioxidant capacity' (TAC), positions it above many other superfoods in combating oxidative damage in the brain and body.
Cacao as a Nootropic
Cacao, a beloved source of indulgence for many, transcends its reputation as the foundational ingredient of chocolate by embodying the qualities of a potent nootropic.
Nootropics, often referred to as "smart drugs" or cognitive enhancers, are substances that can improve cognitive function, memory, creativity, or motivation in healthy individuals.
Within this context, cacao stands out for its natural, multifaceted benefits that support brain health and cognitive performance.
Understanding Nootropics
Nootropics encompass a broad range of natural and synthetic compounds designed to support cognitive health and enhance mental performance.
These substances operate through various mechanisms, such as enhancing neurotransmitter availability, improving blood flow to the brain, and protecting neurons from damage.
Cacao's inclusion in the nootropic category is attributed to its rich array of bioactive compounds, which collectively contribute to its cognitive-enhancing properties.
Cognitive Function and Memory Enhancement
One of the most celebrated aspects of cacao as a nootropic is its capacity to bolster cognitive functions and memory.
Flavonoids, particularly epicatechin found in cacao, have been shown to stimulate brain function by increasing cerebral blood flow.
This enhanced blood flow not only nourishes the brain with vital nutrients and oxygen but also facilitates the removal of toxins and waste products.
Consequently, individuals who regularly consume cacao may experience improvements in cognitive tasks, attention span, reaction times, and memory recall.
Mood Improvement and Stress Reduction
Cacao's influence extends beyond cognitive enhancement to encompass mood regulation and stress reduction.
Tryptophan, an essential amino acid present in cacao, serves as a precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter pivotal in mood regulation.
The consumption of cacao can thus lead to increased serotonin levels, fostering a sense of well-being and happiness.
Additionally, cacao contains phenylethylamine (PEA), a compound that stimulates the release of endorphins and other mood-elevating neurotransmitters.
Through these biochemical pathways, cacao can alleviate stress, reduce anxiety, and promote a positive mental state.
Neuroprotective Properties
The neuroprotective qualities of cacao are among its most significant benefits, offering defense against neurodegenerative diseases and age-related cognitive decline.
The antioxidants in cacao, including flavonoids and polyphenols, combat oxidative stress in the brain, a key factor contributing to neuronal damage.
By neutralizing free radicals and reducing inflammation, these antioxidants can mitigate the risk of developing conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
Furthermore, the neuroprotective effects of cacao extend to enhancing neuronal plasticity, which is crucial for learning, memory formation, and the overall resilience of the brain's neural networks.
Cacao's classification as a nootropic is well-deserved, given its broad spectrum of benefits that promote cognitive health, enhance mental performance, and contribute to emotional well-being.
Its natural composition, rich in neuroactive and neuroprotective compounds, makes cacao an appealing and delicious option for those looking to support their cognitive function and mental health through dietary choices.

Scientific Evidence on Cacao's Benefits
Cacao's role as a nootropic extends far beyond its delightful taste, offering numerous health benefits validated by scientific research.
This section delves into the evidence supporting cacao's effects on cognitive function, stress and anxiety reduction, and cardiovascular health.
Enhancing Cognitive Function
A pivotal aspect of cacao's appeal as a nootropic is its capacity to enhance cognitive function.
Cacao flavonoids, including epicatechin, are capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier, targeting brain areas essential for learning and memory, such as the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and striatum.
These compounds interact with signaling pathways crucial for gene expression and protein synthesis necessary for long-term potentiation (LTP), which underlies long-term memory formation.
Moreover, cacao flavanols have been shown to significantly increase cerebral blood flow, providing neuroprotection and boosting the glucose and oxygen needed by energy-demanding mitochondria.
A comprehensive analysis in "Frontiers in Nutrition" reviewed numerous studies on cacao flavanols, concluding that their cognitive benefits are primarily dose-dependent and most pronounced with long-term daily consumption, enhancing general cognition, attention, processing speed, and memory.
Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Cacao also exhibits potent mood-enhancing properties, attributed to its rich polyphenol content.
A 2012 study focusing on the immediate and long-term effects of cacao polyphenols on cognition and mood found that high doses of cacao polyphenols improved calmness and contentedness among participants.
This study, involving 72 healthy middle-aged individuals, provided a dark chocolate drink mix containing varying levels of polyphenols daily for 30 days, demonstrating significant mood improvement in those receiving the highest polyphenol content.
Benefits for Cardiovascular Health
The cardiovascular benefits of cacao are closely tied to its cognitive enhancing properties.
Flavanols in cacao improve blood flow, not just to the brain, but throughout the entire body, thereby exerting a positive impact on cardiovascular health.
Studies have shown that cacao consumption leads to improved endothelial function, reduced blood pressure, and decreased insulin resistance.
These effects collectively contribute to a reduced risk of stroke and heart disease, further demonstrating the broad spectrum of health benefits provided by cacao.
Enhanced blood flow and oxygenation to the brain, facilitated by cacao's cardiovascular benefits, are crucial for maintaining cognitive function and preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
The scientific evidence surrounding cacao underscores its potential as a powerful natural nootropic and health supplement.
Through its cognitive, mood, and cardiovascular benefits, cacao offers a holistic approach to health and wellness, emphasizing the significance of diet in maintaining and enhancing brain function and overall health.
Health Benefits Beyond Cognition
The allure of cacao extends well beyond its cognitive enhancements, encompassing a wide array of health benefits that contribute to overall wellness.
Renowned for its antioxidant properties, anti-inflammatory effects, and potential to enhance physical endurance and recovery, cacao is a superfood that offers more than just a boost to brain function.
Antioxidant Properties of Cacao
Cacao is packed with powerful antioxidants, primarily flavonoids, which scavenge free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and cellular damage.
This antioxidant activity is pivotal in preventing chronic diseases, aging, and DNA damage.
The flavonoids in cacao, such as epicatechin, catechins, and procyanidins, are especially effective in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby protecting cells from oxidative stress and promoting longevity and health.
Regular consumption of high-flavonoid cacao can contribute to a reduced risk of various diseases, including certain cancers and heart disease, by maintaining cellular health and integrity.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
The anti-inflammatory effects of cacao are another significant health benefit. Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many diseases, including arthritis, heart disease, and diabetes.
The bioactive compounds in cacao can modulate inflammatory pathways in the body, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators.
By inhibiting these inflammatory processes, cacao consumption can help alleviate symptoms of inflammation-related conditions, promoting overall health and wellness.
Potential in Enhancing Physical Endurance and Recovery
Cacao's benefits also extend to physical performance and recovery.
The presence of theobromine, a mild stimulant similar to caffeine but with less impact on the central nervous system, provides a gentle boost in energy and alertness, enhancing physical performance.
Additionally, the antioxidants in cacao contribute to reducing muscle fatigue and improving recovery times by combating oxidative stress induced by exercise.
Cacao also supports cardiovascular health, improving blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles, which is crucial during physical activity.
Moreover, the magnesium content in cacao plays a vital role in muscle function and recovery, further underscoring cacao's potential to support physical endurance and recuperation after exercise.

How to Use Cacao
Integrating cacao into your diet offers a delightful and healthful way to enjoy its myriad benefits.
From enhancing cognitive function to improving cardiovascular health, the versatility of cacao allows for consumption in various forms, each providing a unique experience and benefit.
Understanding how to use cacao, including the recommended dosages and optimal timing, can help maximize its nootropic and health-promoting properties.
Different Forms of Cacao Consumption
Cacao is available in several forms, each suited to different preferences and uses:
- Cacao Nibs: These are crushed cacao beans and one of the most direct ways to consume cacao. They have a rich, chocolatey flavor and can be added to smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal.
- Cacao Powder: Made by grinding cacao beans and removing the fat (cacao butter), cacao powder is ideal for baking or making hot chocolate. It retains most of the antioxidants and minerals found in cacao.
- Dark Chocolate: For those who prefer a more indulgent form, dark chocolate with high cacao content (70% or higher) offers both flavor and benefits. However, it's important to consume in moderation due to added sugars and fats.
- Cacao Butter: Extracted from the cacao beans, cacao butter is the fat portion and can be used in making chocolate or as a dairy-free option in recipes requiring butter.
Recommended Dosages for Health Benefits
While there's no one-size-fits-all dosage for cacao, a general guideline suggests consuming 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 grams) of high-quality dark chocolate or equivalent forms of cacao daily to reap health benefits.
For cacao powder, 2 to 4 tablespoons can provide significant amounts of flavonoids and other bioactive compounds.
It's essential to consider the calorie and fat content, especially when consuming chocolate or cacao butter.
Timing and Combining with Other Supplements
Cacao can be enjoyed at any time of day, though some prefer it in the morning or as an afternoon boost due to its theobromine content, which can provide a gentle, lasting energy lift without the jitters associated with caffeine.
Combining cacao with other supplements can enhance its benefits; for instance, pairing cacao with green tea or curcumin can amplify its antioxidant effects, while combining it with magnesium or omega-3 fatty acids may further support brain health and cognitive function.
To optimize cacao's health benefits, it's advisable to consume it alongside a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
This approach ensures a synergy of nutrients that support overall health and well-being.
Incorporating cacao into your diet offers not only a rich sensory experience but also contributes to a healthier, more vibrant life.
By choosing high-quality cacao products and consuming them in moderation, you can enjoy the delicious and nutritious benefits of this ancient superfood.
Safety and Side Effects
Cacao, celebrated for its extensive range of health benefits, is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation.
However, as with any dietary supplement or food, there are potential side effects and precautions to consider, especially for individuals with certain health conditions or those taking specific medications.
General Safety of Cacao
Cacao is widely regarded as safe for the general population. Its health benefits, including improved heart health, enhanced cognitive function, and mood elevation, are well-documented.
However, cacao contains stimulants such as theobromine and small amounts of caffeine, which could affect sensitive individuals.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While adverse effects are rare, consuming large amounts of cacao can lead to side effects due to its theobromine content, such as insomnia, nervousness, increased heart rate, and digestive issues.
People with caffeine sensitivity should also be cautious, as even the small amounts in cacao can cause symptoms.
Furthermore, high consumption of cacao, especially in the form of commercial chocolate products high in sugars and fats, can contribute to weight gain and associated health issues.
Interactions with Medications and Specific Health Conditions
Cacao's impact on blood pressure and blood sugar levels warrants caution for individuals on medication for hypertension or diabetes, as it could potentiate or inhibit the effects of certain drugs.
Additionally, because of its blood-thinning properties, cacao should be consumed with care by those on anticoagulant medication, as it may increase the risk of bleeding.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women are advised to limit their intake due to the stimulant content and lack of extensive research in these populations.
Importance of Moderation and Consulting with a Healthcare Professional
Moderation is key when incorporating cacao into your diet.
The benefits of cacao are best realized when it is part of a balanced diet without exceeding recommended amounts.
Given the potential interactions and side effects, it's crucial for individuals with existing health conditions or those taking prescription medications to consult with a healthcare professional before significantly increasing cacao consumption.
A healthcare provider can offer personalized advice based on one's health status and dietary needs.
Conclusion
Cacao's journey from an ancient ritualistic element to a modern-day superfood underscores its enduring allure and health-promoting properties.
Cacao serves not just as a culinary delight but as a potent nootropic and wellness enhancer, offering cognitive benefits, mood improvement, stress reduction, and neuroprotective properties.
Beyond cognition, its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, alongside the potential to enhance physical endurance and recovery, position cacao as a holistic supplement for overall health.
The versatility of cacao allows for its integration into daily routines in various forms, from cacao nibs and powder to dark chocolate, each offering a unique blend of benefits.
Whether for boosting memory, reducing stress, or simply enjoying a healthier treat, cacao stands out as a valuable ally in the pursuit of health and happiness.
Are you considering joining the ranks of those who have experienced the cognitive benefits of nootropics? To learn more about how our Mood & Wellbeing Nootropic Supplement might fit into your lifestyle, visit us at nooroots.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is organic cacao?
Organic cacao is raw, minimally processed chocolate derived from the seeds of the cacao tree, known for its rich antioxidant content and cognitive-enhancing properties.
How does organic cacao work as a nootropic?
Organic cacao enhances cognitive function by increasing blood flow to the brain, providing antioxidant protection, and stimulating the production of feel-good neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
Can organic cacao improve memory?
Yes, organic cacao can improve memory and cognitive performance by promoting neurogenesis and enhancing blood flow to the brain.
Is organic cacao safe for daily use?
Organic cacao is generally safe for daily use in moderate amounts. It’s advisable to monitor intake due to its caffeine content and potential calorie contribution.
What are the benefits of organic cacao for the brain?
Organic cacao supports brain health by providing antioxidants, improving mood, enhancing memory, and increasing focus and alertness.
How much organic cacao should I take for cognitive benefits?
Typical dosages for cognitive benefits range from 10 to 40 grams per day, depending on the concentration of cacao and individual tolerance.
Are there any side effects of taking organic cacao?
Some individuals may experience side effects such as jitteriness, digestive issues, or headaches, particularly if consumed in large amounts due to its caffeine content.
Can organic cacao help with anxiety and depression?
Yes, organic cacao can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by boosting serotonin and endorphin levels, promoting a sense of well-being.
What is the best way to take organic cacao for nootropic effects?
Organic cacao can be consumed as raw cacao nibs, powder, or dark chocolate with a high percentage of cacao. It can be added to smoothies, beverages, or used in baking.
How long does it take to see the effects of organic cacao on cognitive function?
The cognitive benefits of organic cacao can typically be felt within 30 minutes to an hour after consumption, with effects lasting for several hours.
Learn more about the vitamins, minerals and plant extracts we use to give your brain a daily boost
- Cacao
- Ginkgo Biloba
- Ashwagandha
- N-Acetyl L-Tyrosine
- Holy Basil
- L-Theanine
- Rhodiola Rosea
- Guarana Seed
- Piperine
References
- Baker, L.D. et al. (2022) 'Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial,' Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 19(4), pp. 1308–1319. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12767.
- Katz, D.L., Doughty, K.N. and Ali, A. (2011) 'Cocoa and chocolate in human health and disease,' Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 15(10), pp. 2779–2811. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3697.
- Martín, M.Á., Goya, L. and De Pascual‐Teresa, S. (2020) 'Effect of cocoa and cocoa products on cognitive performance in young adults,' Nutrients, 12(12), p. 3691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123691.
- Nehlig, A. (2013) 'The neuroprotective effects of cocoa flavanol and its influence on cognitive performance,' British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 75(3), pp. 716–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04378.x.
- Nemoto, K. et al. (2022) 'Dark chocolate intake may reduce fatigue and mediate cognitive function and gray matter volume in healthy Middle-Aged adults,' Behavioural Neurology, 2022, pp. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6021811.
- Scherma, M. et al. (2018) 'Brain activity of anandamide: a rewarding bliss?,' Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 40(3), pp. 309–323. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0075-x.
- Socci, V. et al. (2017) 'Enhancing Human Cognition with Cocoa Flavonoids,' Frontiers in Nutrition, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2017.00019.
- Tartar, J.L. et al. (2021) 'An evaluation of the effects of a non-caffeinated energy dietary supplement on cognitive and physical performance: a randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled study,' Cureus [Preprint]. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.16178.
- Zeli, C. et al. (2022) 'Chocolate and Cocoa-Derived Biomolecules for Brain Cognition during Ageing,' Antioxidants, 11(7), p. 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071353.